Indexed Pagesplay a pivotal role in the realm of search engine optimization (SEO). They are the cornerstone upon which the entire structure of online visibility and ranking is built.
The pages of a website that have been seen, examined, and added to a search engine's collection of web pages are known as indexed pages. Sites are indexed either after the website owner asks the search engine to do so or after the search engine bot finds them through links to those sites.
This article will delve into the importance of Indexed Pages, how search engines index web pages, and the strategies to ensure your web pages are effectively indexed for optimal SEO results?
The Basics Of Indexed Pages
One of the fundamental aspects of understanding Indexed Pages is recognizing the lifecycle they go through. It's more complex than a page being either indexed or not; there are several stages in the journey to becoming a fully indexed page. This process involves crawling, rendering, and indexing.
Crawling - The First Step To Indexing
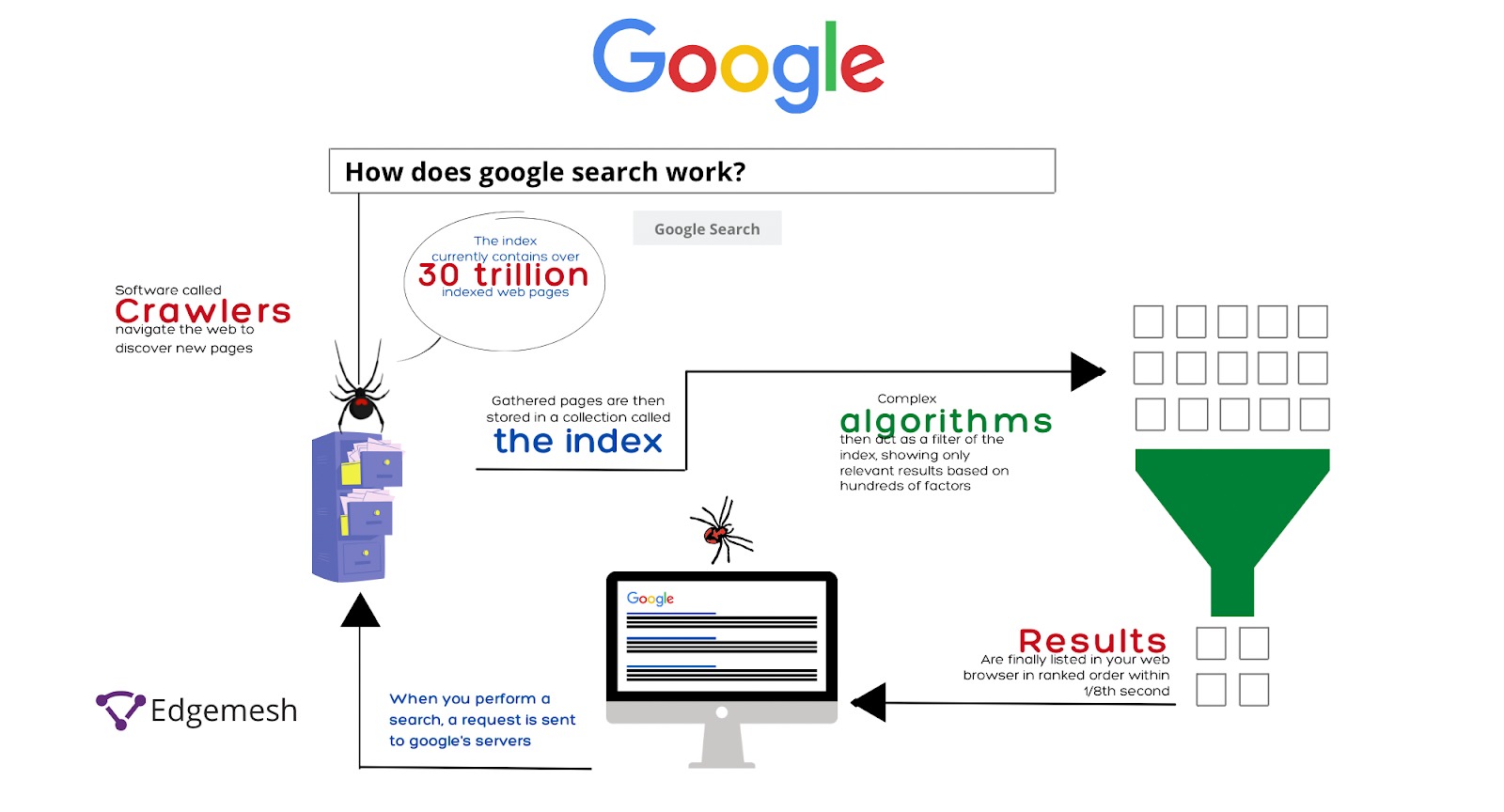
Crawling is the initial phase in the indexing process. Search engine crawlers, also known as spiders or bots, systematically traverse the internet to discover and gather information about web pages. They start with a set of known web pages, follow links to new pages, and continue this process recursively.
During crawling, these bots request pages from web servers, parse HTML and other resources, and add the discovered pages to their queue for further processing. However, it's essential to understand that not all crawled pages make it to the indexing phase. Various factors come into play that can determine whether a page progresses or remains in limbo.
Rendering - Ensuring A Page's Readiness
After a page is crawled, the next step is rendering. During rendering, the search engine bot attempts to view the page as a human user would. This step is vital to ensure that the page is correctly loaded and that any dynamic content, JavaScript, or AJAX requests are appropriately executed.
Rendering is especially crucial for web pages with JavaScript-driven content, as search engines have evolved to render such content for indexing. If a page does not render correctly, it may not be indexed accurately, leading to issues with how the page appears in search results.
Indexing - The Final Destination
The final and most significant step in the journey of Indexed Pages is the indexing itself. After a page is crawled and rendered successfully, it is processed and added to the search engine's index. This means that the page becomes part of the vast database of pages that search engines can retrieve when users enter relevant queries.
The indexing process involves extracting critical information from the page, such as the page's title, meta description, headings, and the content itself. This information is then stored in the search engine's index, making it available for retrieval in search results.
How To Do Page Indexing In Google?
The most popular search engine worldwide is Google. Google has already surpassed the 50% use mark, even in nations with a robust domestic focus like Russia, where Yandex.com has been a household brand for a long time. Webmasters would want Google to index their sites, articles, and other content as fast as possible.
Imagine that you have recently created a new e-shop, renamed it, and moved it to a new domain and that you sell seasonal items or time-sensitive content, such as at the start of the school year, around Christmas, or during the summer breaks. How appreciated is that early Google indexing when the future of your company depends on it?
There are various strategies to aid you in this predicament by getting your sites or new material indexed quickly. However, the following two methods are the quickest and most likely to be successful of all.
Therefore, you can select one of the following stages or combine them. Whatever you choose to do, these steps will enable you to set up the conditions for quick content indexing, which is a precondition for generating early visitors.
How Long Does It Take For Google To Index A Website?
To ensure your content gets indexed, the initial step involves facilitating its crawling. The duration required for your website to undergo a complete crawl operation hinges on your crawl budget, which signifies the level of attention your site receives from Google.
Following successful crawling, the subsequent phase is indexing. During this stage, the pace of indexing is influenced significantly by the following factors:
- The extent to which your website relies on client-rendered JavaScript.
- The quality of your content.
- The overall size of your website.
As a general guideline, we typically provide the following estimates:
- For websites with fewer than 500 pages, the indexing process usually takes 3–4 weeks.
- Websites containing 500 to 25,000 pages typically require 2–3 months for indexing.
- In the case of websites exceeding 25,000 pages, indexing may span from 4 to 12 months.
It's important to note that each website is unique and is subject to individual handling by Google. Consequently, it's advisable to consider these estimates as rough approximations. Ultimately, Google holds the ultimate authority in all matters related to SEO.
What Are Non-indexed Web Pages?
Non-indexed web pages are web pages that have not been included in a search engine's index. Search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo use automated programs called web crawlers or spiders to discover and index web pages on the internet. When a web page is indexed, it means that the search engine has added the page to its database and can retrieve it in response to user search queries.
There Are Several Reasons Why A Web Page Might Not Be Indexed:
- Robots.txt Exclusion -Webmasters can use a file called "robots.txt" to instruct search engine crawlers on which parts of their website should not be indexed. If the robots.txt file blocks a web page, it won't be indexed.
- No-Follow Tags -Some web pages include a "no-follow" meta tag or attribute in their HTML code, which tells search engines not to follow any links on that page. If a page is not followed, it may not be indexed.
- Low Quality or Duplicate Content -Search engines may choose not to index web pages with low-quality content, duplicate content, or content that appears to be spammy.
- New or Unpopular Pages -It can take some time for search engine crawlers to discover and index new web pages. If a page is on a relatively unknown or unpopular website, it may not be indexed quickly or at all.
- Technical Issues -Technical issues on a website, such as server errors, can prevent search engine crawlers from indexing web pages.
- Manual Removal -In some cases, a website owner or webmaster may request that a specific page be removed from a search engine's index. Search engines may comply with such requests.
It's important for website owners and administrators to ensure that search engines index their important and relevant web pages, as this is crucial for visibility in search results. Conversely, if a web page contains sensitive or private information that should not be publicly accessible, steps should be taken to prevent indexing by search engines.
Why Indexed Web Pages Are Essential?
Page indexing and search engine optimization have more moving parts than would at first seem. To begin, if you want to achieve desired search engine rankings, URL indexing is required. No matter how well you optimize a website, the search engine's ranking and user traffic will not improve if the page is not indexed.
That's why it's just the indexed sites that get a guaranteed spot in the SERP. However, the precise placement will be determined by the total of all on-page and off-page SEO elements that you have optimized for up to that point. Yes, your indexing will shift if you forget about your site for too long.
In addition to these, there are more variables that we may influence to varying degrees. We refer to the following variables:
- Content publication rate;
- Content quality;
- Site updates;
- Existing competition
Quantitative indexing similarly influences a page's SEO ranking. When compared to rival websites, those with a larger number of indexed URLs under the same domain rank higher. Quantity is not the only essential aspect thus, this assumes that these URLs are also high-quality.
For URLs to be found by search engines and, therefore, found by potential consumers interested in your product or service, they must be indexed.
Web pages won't be found and, as a result, will only rank if they are given the assignment to be indexed - ranking and Domain Authority for a URL change over time. There are additional elements at work in addition to the need for ongoing optimization.
Navigating The Web - A Search Engine's Guide
Imagine the World Wide Web as an enormous library with an ever-expanding collection of books, each representing a web page. Search engines are the librarians tasked with categorizing and indexing this vast repository of knowledge. Indexed web pages, in this analogy, are the library's index, helping users find the information they seek efficiently.
Indexed pages are readily available to users when they enter search queries. Without them, finding specific information on the web would be akin to searching for a needle in a haystack. Their presence makes web navigation straightforward and accessible.
With billions of web pages in existence, not all of them can be manually discovered and explored. Indexed pages allow users to access a diverse range of content, from educational articles and news reports to product listings and entertainment.
Fueling Organic Traffic
Webmasters and businesses invest considerable effort in creating and optimizing web content. The goal is not merely to have a presence on the web but to attract visitors who are genuinely interested in the content or products offered. Indexed pages play a pivotal role in this process.
Indexed pages are the ones that appear in search engine results pages (SERPs) when users input relevant search queries. For webmasters, being indexed means their content has a chance to be seen and clicked on by potential visitors.
Organic traffic, the type of traffic that arrives at a website through search engine results, is precious. It often consists of users actively seeking specific information or products, making them more likely to engage and convert.
Catering To Diverse User Queries
The internet caters to a global audience with an array of interests and needs. Indexed web pages offer a solution for a broad spectrum of user queries.
Indexed pages allow webmasters to target a multitude of long-tail keywords – specific and less competitive search terms. This strategy can be highly effective in reaching niche audiences and providing solutions tailored to their needs.
Websites with a robust portfolio of indexed pages that address various facets of their niche establish themselves as authorities in their field. This, in turn, fosters trust among users.
Enhanced User Experience
A well-structured website with a wealth of indexed pages contributes to an improved user experience. This, in turn, benefits both the website and its visitors.
Users who find the information they seek are less likely to leave a website immediately, resulting in lower bounce rates. Indexed pages offer an extensive array of content, reducing the chances of visitors going due to a lack of relevant information.
Indexed pages create opportunities for effective internal linking, guiding users to related content and facilitating seamless navigation.
Factors That Influence Indexing
Indexing is a dynamic process where search engines determine which web pages should be included in their vast databases, making them accessible through search results.
Content Quality - The Foundation Of Indexing
At the core of indexing is the quality of web content. Search engines are committed to delivering valuable and relevant content to users. Hence, they consider content quality as a primary factor in the indexing process.
Search engines prefer content that is original and unique. Duplicate or heavily copied content may not be indexed, as it doesn't contribute additional value to users.
The indexing process is fueled by the relevance of content to user queries. Pages that provide solutions, answers, or valuable information are indexed more frequently.
Search engines favor websites that consistently update their content. Frequent updates signal an active and valuable resource, encouraging indexing.
Metadata Optimization - Communicating With Search Engines
Metadata, including title tags and meta descriptions, plays a pivotal role in indexing. These elements provide search engines with essential information about web pages.
Title tags are displayed in search results and are a primary factor in determining the subject matter of a web page. Optimizing title tags with relevant keywords can improve indexing.
Meta descriptions provide a summary of a page's content. Well-crafted meta descriptions can entice users to click on a search result and can influence indexing by improving click-through rates.
Technical Considerations - Navigating The Digital Landscape
Several technical aspects of a website can influence indexing. Webmasters need to address these considerations to enhance the likelihood of their pages being indexed.
The robots.txt file instructs search engines on which pages should not be crawled or indexed. Properly configuring the robots.txt file can prevent sensitive or duplicate content from being indexed.
XML sitemaps serve as a roadmap for search engine crawlers. They provide a structured overview of a website's content, helping crawlers navigate and understand the site better. Submitting sitemaps to search engines can influence the indexing process.
With Google's mobile-first indexing approach, ensuring that a website is mobile-friendly is vital. A mobile-responsive design not only enhances user experience but also improves indexing for mobile search results.
Website speed and performance directly impact indexing. Slow-loading pages can deter search engines from indexing them. Optimizing page speed is crucial for SEO success.
How To Find Pages Indexed By Google?
Knowing which of your web pages are indexed by Google is a crucial aspect of monitoring your website's performance and visibility in search results.
To Check Indexed Web Pages Via Search Engine Results
- Enter the name of your website in the search field while you are on Google or another search engine. Take "JanBask Digital Design" as an illustration.
- You will notice some numbers next to the "results" when you enter your website's URL in the search field. These numbers indicate how many websites Google has indexed.
You can follow these steps to check the URL index status of a specific web page.
- Enter the website address or page name. For example, enter "janbaskdigitaldesign.com/portfolio."
- Once more, you will see some numbers next to the word "results." If your website still needs to be indexed, keep in mind that no results will appear.
Checking Indexed Web Pages Via Google Search Console Report
You may use Google Search Console's Index Coverage Status Report to get thorough information about the index status of your web pages.
- Go to Google Search Console, choose "index," then select "coverage."
- The part of a legitimate page (with both a warning and without one) may be found there.
- Your specific web pages appear to be correctly indexed in Google if the sum of these legitimate pages is more than zero.
Suppose you are having trouble successfully indexing your website on Google or are stuck with the "non-indexed" page status. In that case, you can hire one of the top SEO agencies, or you can follow our list of easy steps to submit your web pages to Google Webmaster Tools successfully and have them indexed by Google Checker right away.
How To Check If A Page Is Indexed
To determine whether a page is indexed or not, you can follow these methods:
Google Search Console (Recommended)
- Add your website to Google Search Console if you haven't already.
- Use the 'URL inspection' tool within Google Search Console.
- Enter the URL of the webpage you want to check.
- Google Search Console will provide information on whether the page is indexed or not.
Use Google’s "site:" Search Operator
- Go to Google's search bar.
- Enter the following command: site:yourwebpageURL.
- If your page appears in the search results, it's likely indexed.
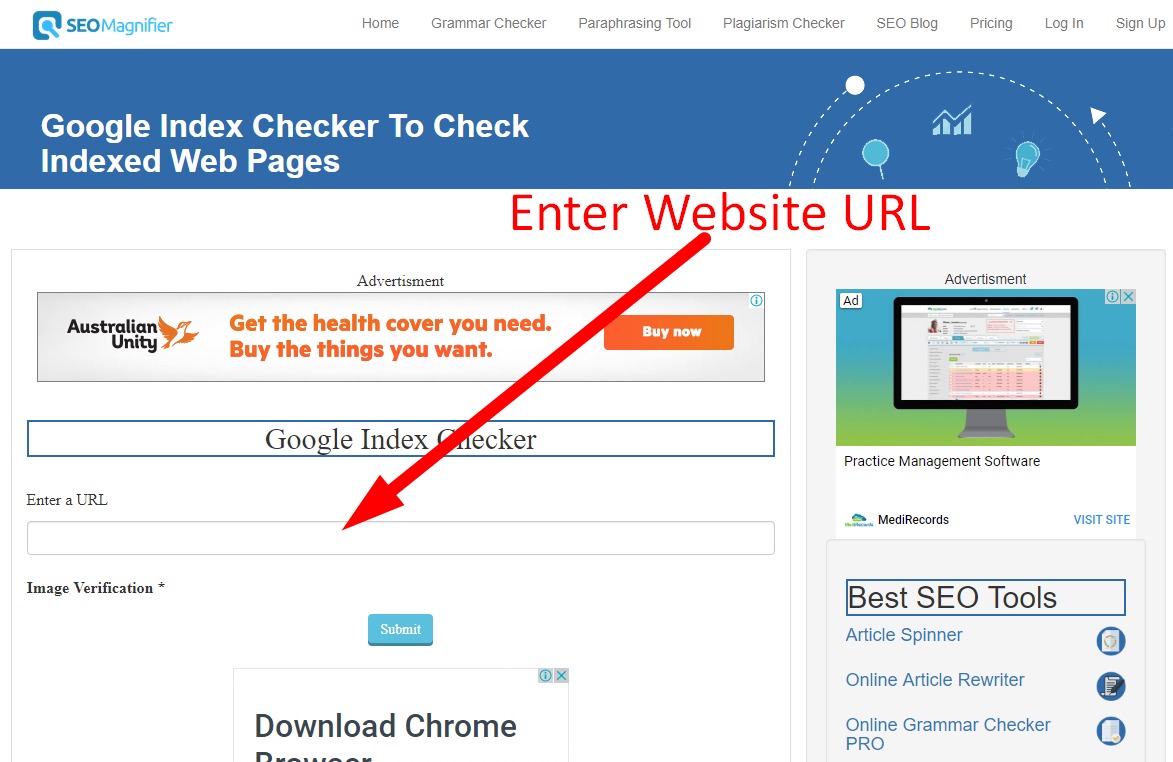
Indexed Pages Checker Tools
- You can use online tools such as Semrush or SE Ranking to check the indexing status of your webpage.
- Input the URL of your webpage, and these tools will report whether the page is indexed.
- Remember, if your page is not indexed, it won't show up in Google's search results. Ensuring that all your important pages are indexed is crucial for their visibility on the web.
3 Most Popular Indexed Page Checkers Tools
In addition to the ways already discussed, there are also several third-party programs available for checking Google's index.
There are three of them that stand out as the most popular:
Small SEO Tools
The Index Checker Tool is only one of several in our collection of SEO utilities. It's useful since it lets you check up to five URLs simultaneously.
Duplichecker
In addition to being a tool for detecting plagiarized content, they also provide an index checker that can examine ten URLs simultaneously.
Website SEO Checker
Once again, an SEO audit tool should have an index checker as part of its overall suite of features. To check your URL, go to their site, paste it into the search field, input the captcha code they provide, and click the "Check" button.
Indexed Pages - FAQs
What Is The Primary Purpose Of Indexing Web Pages?
Indexing web pages allows search engines to make them accessible to users in search results.
How Does Google Determine Which Pages To Index?
Google's search algorithms consider factors like content quality, relevance, and backlinksto determine which pages to index.
Why Is Avoiding Duplicate Content Crucial For Indexed Pages?
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and lead to indexing issues, affecting a website's search performance.
What Role Do XML Sitemaps Play In Indexing Web Pages?
XML sitemaps provide a structured overview of a website's content, helping search engine crawlers navigate and understand the site for indexing purposes.
How Can Webmasters Check The Indexing Status Of Their Pages Using Google Search Console?
Google Search Console provides an Index Coverage report and a URL Inspection tool to monitor the indexing status of web pages.
Conclusion
The significance of "Indexed Pages" cannot be overstated in the realm of SEO. They serve as the foundational bricks of your online presence, offering the gateway for users to discover your web content through search engines like Google.
Understanding the factors that influence the indexing of your pages, ensuring their quality and relevance, and employing tools and methods to track their status are essential steps in optimizing your website's performance.
Whether through Google's search operators, Search Console, or third-party tools, monitoring your "Indexed Pages" empowers you to enhance your website's visibility, drive organic traffic, and achieve success in the competitive digital landscape.